The Belgian food safety authorities have insisted the risk of domestic pigs becoming infected with African swine fever remains ‘limited’, despite the virus being confirmed in wild boar.
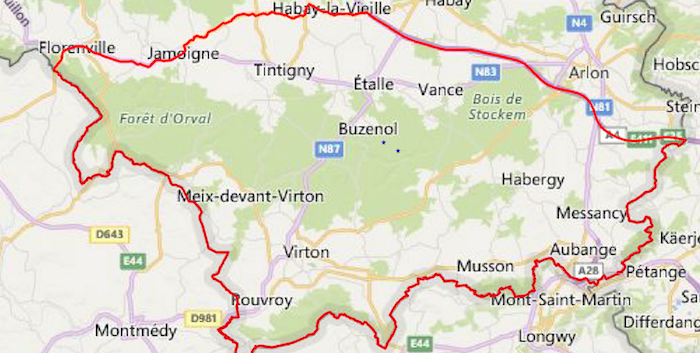
ASF was confirmed for the first time in Belgium since 1985 on Friday in two wild boar in Etalle, in the province of Luxembourg, just a few miles from the French border. It has since been confirmed in more wild boar in the region.
Belgium’s Federal Agency for the Safety of the Food Chain said there were no outbreaks in domestic pigs. It said ‘very few’ domestic pigs are kept in this region, with most pig farms are located in the northern part of Belgium.
Belgium currently still has disease free status for domestic and captive wild pigs, although it has lost its disease-free status for ASF ‘in all suids’, under the OIE Terrestrial Code, the agency said.
The agency said: “It should be emphasized that the potential risk lies in the spreading from wild boars to domestic and captive wild pigs, but that this risk is quite limited since the necessary measures are taken. The consumer himself is not at risk.
“African swine fever is momentarily limited to wild boars (no outbreaks in domestic swine), and the necessary measures are taken regarding these cases to control and avoid dissemination of the disease.”
“Notwithstanding, the certification conditions laid down in the relevant protocols concluded between Belgium and the non-EU countries (third countries) will be scrupulously respected.”
The UK Animal and Plant Health Agency has warned, however, that the cases reported in wild boar are ‘concerning’ given the large numbers of wild boar in this forested area, crossing EU borders. “Eradication will be a challenge to be met through close collaboration and information sharing between those Member States at risk,” it said.
The infected area has been established, as can be seen here and here
Various measures have been put in place, under the EU protocol for ASF outbreak. In the infected zone, the following measures are being taken:
- Monitoring of wild boars in order to get a picture of the situation
- Limiting hunting to avoid dissemination
- Limiting human activities in forest
- Monitoring pig farms
- Complete separation of swines and wild boars
- Movements (to/from) of swines only with the authorization of the competent authority
- Increasing biosecurity
- Analysis of all sickness/death
Measures are also being enforced throughout the country to reduce the risk of spreading, including:
- A ban on assembling of pigs
- Ensuring domestic pigs avoid contact with wild boars
- Increased biosecurity for the entire sector
- Increased surveillance.
The agency has also started an epidemiological investigation to identify the cause of the ASF virus introduction.